ERNIE - 清华 详解
ERNIE: Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities 提出了将知识显性地加入到BERT中。值得注意的是,百度也出了名为ERNIE的模型,且影响力更大,但是百度的知识是通过MASK的方式隐性的加入的。

清华ERNIE的模型通过更改模型结构,将知识和语言语义信息融合,增强了语义的表示,在知识驱动的任务中取得了显著的成功。这个模型的结构给我的感觉是和华为的ZEN很类似,但是目前看效果是没有华为的ZEN好,ZEN采用的是将N-gram而不是Entity加入到模型中,以及融合的时候也有区别。
那么我们如何将文本信息中的知识提取出来,然后再将这些知识和BERT的上下文语义embedding进行结合,这就是本文主要需要解决的问题。 key point:
- 首先提取输入文本的named entity,经过构造KG,然后通过TransE的方式将named entity进行embedding,经过Knowledge Encoder of ERNIE,得到的结果和 Text Encoder of Ernie进行align,再经过信息融合,得到两种输出,Token output以及Entity output。
- 目标函数有MLM,NSP以及针对Kg制定的mask entity prediction
Model Architecture
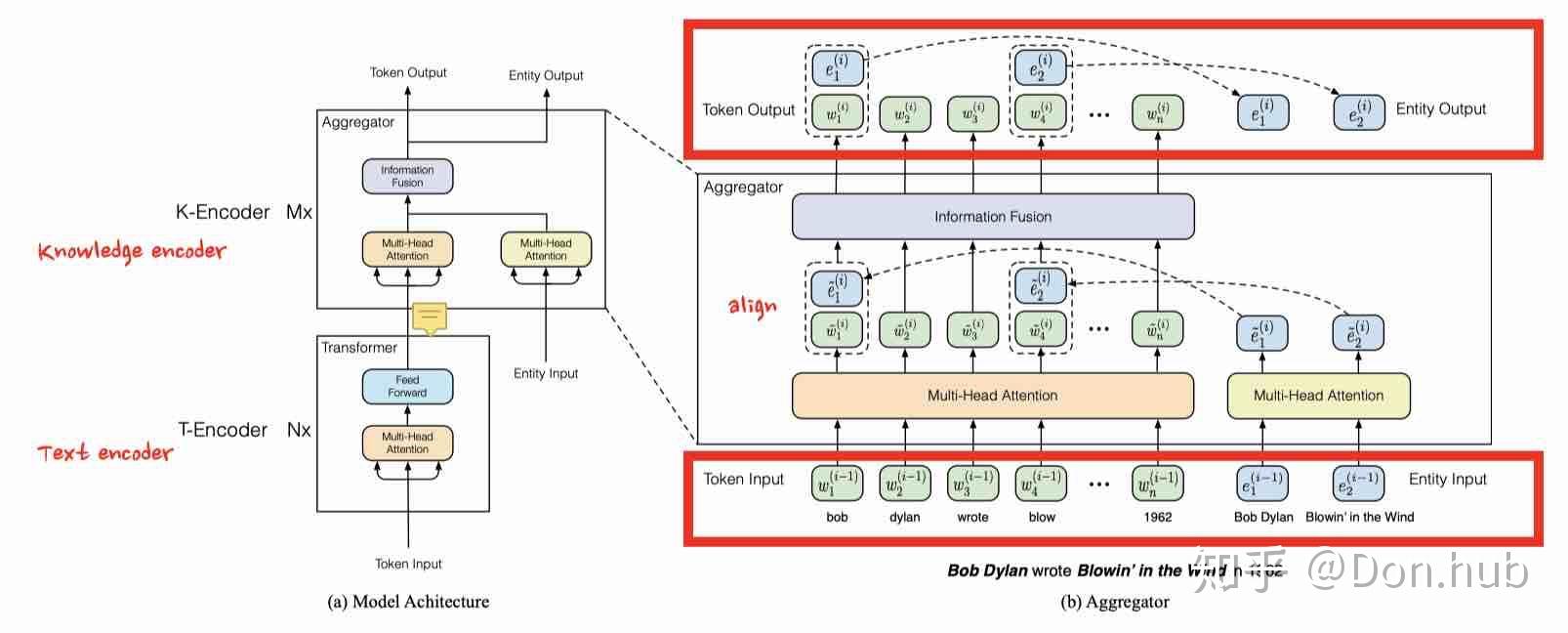
模型主要有两种Encoder组成,分别是T-Encoder以及K-Encoder。 其中T-Encoder主要是进行输入文本的encoder,提取的是词法以及语义的信息。共N层。 而K-Encoder主要进行的是知识entity的embedding以及知识融合。共M层
输入文本 {w_1, ..., w_n} (均为subword level), entity embedding {e_1, ..., e_m} , 其中m往往小于n。
其中entity embedding使用的是transE embedding,即构建(H,R,T), 模型得到对应的relation embedding以及entity embedding。
- TransE

Title:Translating Embeddings for Modeling Multi-relational Data(2013) This is the first work of the translation model series. The basic idea of this model is making the sum of the head vector and relation vector as close as possible with the tail vector. Here we use L1 or L2 norm to measure how much they are close.
The loss function is the max-margin with negative sampling. L(y, y’) = max(0, margin -y + y’) y is the score of a positive sample, and y' is the score of a negtive sample. Minimizing this loss function score. It is enough that the difference between the two scores is as large as margin (we set this value, usually is 1). Because we use distance to represent the score, so we add a minus to the equation, the loss function for knowledge representation is: L(h,r,t) = max( 0, d_{pos} - d_{neg} +margin)
And d is: ||h+r-t||
This is the L1 or L2 norm. As for how to get the negative sample is replacing the head entity or tail entity with a random entity in the triple. See the code:

Using embedding_lookupget the vector of the head, relation, tail, and calculate the distance between (head, relation) and tail. But this model only can take care with one-to-one relation, not suitable for one-to-many/many-to-one relation, for example, there is two knowledge, (skytree, location, tokyo) and (gundam, location, tokyo). After training, the 'sky tree' entity vector will be very close with 'gundam' entity vector. But they do not have such similarity in real.
模型主要的作用:
\begin{equation} {\omega _1, ..., \omega_n} = T-Encoder({w_1, ..., w_n}) \tag1 \end{equation}
\begin{equation} \{\omega _1 ^o, ..., \omega_n ^o\}, \{e_1^o, ..., e_m^o\}= K-Encoder(\{\omega _1, ..., \omega_n\}, \{e_1, ..., e_m\}) \tag2 \end{equation}
Structured Knowledge Encoding(Knowledge Encoder)
对于一句话的输入,例如
bob dylan wrote Blowin' in the wind
首先提取出模型中的的entities,bob dylan 和 Blowin' in the wind作为entities
注意这边的进行了token embedding以及entity embedding的multi-head self-attentions(MH-ATTs)。
\begin{equation} \begin{split} \{\tilde w_1^{(i)}, . . . , \tilde w_n^{(i)}\} = MH-ATT(\{w_1^{(i−1)}, . . . , w_n^{(i−1)}\}), \\ \{\tilde e_1^{(i)}, . . . , \tilde e_n^{(i)}\} = MH-ATT(\{e_1^{(i−1)}, . . . , e_n^{(i−1)}\}) \end{split} \tag3 \end{equation}
在这之后第i个aggregator采用了information fusion layer将两个信息进行了融合,这边不是采用简单的向量相加得到一个向量,而是先combine后divide的方式,分别得到新的token embedding以及entity embedding。(2层的dense)
\begin{equation} \begin{split} h_j &= \sigma (\tilde W_t^{(i)} \tilde \omega _j ^{(i)} + \tilde W_e^{(i)} \tilde e _k ^{(i)} + \tilde b^{(i)}) \\ \omega _j {(i)} &= \sigma(W_t ^{(i)} h_j + b _t ^{(i)}),\\ e_k ^{(i)} &= \sigma( W_e ^{(i)} h_j + b_e ^{(i)}) \end{split} \tag4 \end{equation}
其中 e_k = f(w_j) , 指的是一个token w_j 和它aligned的entity e_k ,这边的aignment函数是指的是entity的首个token进行align。
对于没有对应的entity的token,information infusion layer的输出就是两层的dense,跟正常一样。
\begin{equation} \begin{split} h_j &= \sigma (\tilde W_t^{(i)} \tilde \omega _j ^{(i)} + \tilde b^{(i)}) \\ \omega _j {(i)} &= \sigma(W_t ^{(i)} h_j + b _t ^{(i)}) \end{split} \tag5 \end{equation}
Pretraining for Injecting Knowledge
为了更好的训练模型,ERNIE提出了一种denoising entity auto-encoder(dEA),主要的做法是随机mask一些token-entity alignments 然后要模型根据aligned tokens w_i 去预测entities e_k 。
\begin{equation} \begin{split} p(e_j|w_i) = \frac {exp(linear(w_i^o)· e_j))} {\sum _{k=1} ^m exp(linear(w_i^o)·e_k)} \end{split} \tag6 \end{equation}
考虑到有可能存在错误的token-entity alignmnent,具体操作
- 5%的时间,对于一个token-entity alignmnent,随机替换entity,让模型预测正确的entity
- 15%的时间,随机mask掉 token-entity alignmnents,让模型去正确预测token-entity alignment。
- 剩下的时间,token-entity alignmnents不变,让模型将知识进行融合。
Fine-tuning for Specific Tasks

对于普通的分类任务,采用的仍然是[CLS]作为输出 对于knowledge driven的任务,比如说
- relation classification 增加[ENT] token
- entity typing 增加[HD][TL] token
限制
依赖于NER提取的准确度 模型复杂度过高

