从零开始手敲次世代游戏引擎(八十三)
本篇我们来实现游戏内交互界面(GUI)
游戏内GUI的实现可以有很多选择,我这里选用轻量级并且支持多平台的Dear ImGui。因为它整体上的结构与我们的引擎比较契合。
这个Dear ImGui在业界也十分有名,其脱胎于PSV的Tearaway这款游戏,之后由原作者进行了大量的整理扩展工作,在诸如育碧的《刺客信条 奥德赛》《刺客信条 起源》、索尼的《拯救宇宙机器人》、SE的《FFVII重制版》、Mojang的《我的世界(Bedrock)》、暴雪的《Warcraft III: Reforged》等等知名游戏当中都有应用。同时也被集成在UE、Unity、Cocos2D等知名引擎当中。
Dear ImGui以一组自包含的源代码形式提供。其本身封装了GUI部件的状态逻辑与控制,通过一个被称为ImGui::IO的模块与外部进行通信,包括获取用户输入以及输出渲染指令。Dear ImGui本身是平台及图形渲染API无关的。使用者需要将平台的用户输入事件转换传递给ImGui::IO,然后将ImGui::IO当中保存的平台无关绘图命令队列转换成具体的图形渲染API队列。
不过,因为大量成熟项目的应用,Dear ImGui自身已经相当稳定,并且随代码提供了一系列常见平台和图形API的绑定源代码。这些代码以代码片段的方式提供,可以很容易插入到我们自己的工程当中。
Officially maintained bindings (in repository):
Renderers: DirectX9, DirectX10, DirectX11, DirectX12, OpenGL (legacy), OpenGL3/ES/ES2 (modern), Vulkan, Metal.
Platforms: GLFW, SDL2, Win32, Glut, OSX.
Frameworks: Emscripten, Allegro5, Marmalade.
Third-party bindings (see Bindings page):
Languages: C, C#/.Net, ChaiScript, D, Go, Haskell, Haxe/hxcpp, Java, JavaScript, Julia, Kotlin, Lua, Odin, Pascal, PureBasic, Python, Ruby, Rust, Swift...
Frameworks: AGS/Adventure Game Studio, Amethyst, bsf, Cinder, Cocos2d-x, Diligent Engine, Flexium, GML/Game Maker Studio2, GTK3+OpenGL3, Irrlicht Engine, LÖVE+LUA, Magnum, NanoRT, Nim Game Lib, Ogre, openFrameworks, OSG/OpenSceneGraph, Orx, Photoshop, px_render, Qt/QtDirect3D, SFML, Sokol, Unity, Unreal Engine 4, vtk, Win32 GDI, WxWidgets.
Note that C bindings (cimgui) are auto-generated, you can use its json/lua output to generate bindings for other languages.
Also see Wiki for more links and ideas.
接下来我们来实际操作一下。
首先是将Dear ImGui的Repository加入我们的外部模块当中:
git submodule add --name imgui https://github.com/ocornut/imgui.git External/src/imgui代码签出之后,我们用tree命令看一下它的构造:

虽然有不少的代码,但是其实Dear ImGui自身只是顶层目录下的那几个文件(上图最下方)。examples下面的文件都是各个平台及图形API绑定的参考代码,并不是Dear ImGui的主体部分。
Dear ImGui将自身也划分成3个层面:平台、图形API、核心。这种划分与我们的引擎十分接近。因此,我们首先在引擎的平台对接层完成Dear ImGui的Binding的对接:
Platform/Windows/WindowsApplication.cpp
#include "imgui/examples/imgui_impl_win32.h"
void WindowsApplication::CreateMainWindow() {
// get the HINSTANCE of the Console Program
HINSTANCE hInstance = GetModuleHandle(NULL);
// this struct holds information for the window class
WNDCLASSEX wc;
// clear out the window class for use
ZeroMemory(&wc, sizeof(WNDCLASSEX));
...
// display the window on the screen
ShowWindow(m_hWnd, SW_SHOW);
// Initialize ImGui
IMGUI_CHECKVERSION();
ImGui::CreateContext();
[[maybe_unused]] ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
ImGui_ImplWin32_Init(m_hWnd);
ImGui_ImplWin32_EnableDpiAwareness();
ImGui::StyleColorsDark();
}
void WindowsApplication::Finalize() {
// Finalize ImGui
ImGui_ImplWin32_Shutdown();
ImGui::DestroyContext();
ReleaseDC(m_hWnd, m_hDc);
BaseApplication::Finalize();
}
extern IMGUI_IMPL_API LRESULT ImGui_ImplWin32_WndProcHandler(HWND hWnd,
UINT msg,
WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam);
// this is the main message handler for the program
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowsApplication::WindowProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) {
LRESULT result = 0;
WindowsApplication* pThis;
if (message == WM_NCCREATE) {
pThis = static_cast<WindowsApplication*>(
reinterpret_cast<CREATESTRUCT*>(lParam)->lpCreateParams);
SetLastError(0);
if (!SetWindowLongPtr(hWnd, GWLP_USERDATA,
reinterpret_cast<LONG_PTR>(pThis))) {
if (GetLastError() != 0) return FALSE;
}
} else {
pThis = reinterpret_cast<WindowsApplication*>(
GetWindowLongPtr(hWnd, GWLP_USERDATA));
}
// ImGui message handler
result = ImGui_ImplWin32_WndProcHandler(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
// sort through and find what code to run for the message given
switch (message) {
case WM_CHAR: {
g_pInputManager->AsciiKeyDown(static_cast<char>(wParam));
} break;
case WM_KEYUP: {
...
// this message is read when the window is closed
case WM_DESTROY: {
// close the application entirely
PostQuitMessage(0);
m_bQuit = true;
} break;
default:
// Handle any messages the switch statement didn't
result = DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return result;
}
上面加粗的部分就是新插入的ImGui的代码片段。可以看到对我们程序原本的结构基本没有任何破坏,非常干净。
接下来,是在图形API环境,也就是我们的RHI当中,插入ImGui图形API绑定的相关代码:
RHI/OpenGL/OpenGLGraphicsManager.cpp
#include "imgui/examples/imgui_impl_opengl3.h"
#ifdef OS_WINDOWS
#include "imgui/examples/imgui_impl_win32.h"
#endif
int OpenGLGraphicsManager::Initialize() {
int result;
result = OpenGLGraphicsManagerCommonBase::Initialize();
if (result) {
return result;
}
result = gladLoadGL();
...
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_Init("#version 420");
return result;
}
void OpenGLGraphicsManager::Finalize() {
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_Shutdown();
OpenGLGraphicsManagerCommonBase::Finalize();
}
void OpenGLGraphicsManager::BeginFrame(const Frame& frame) {
OpenGLGraphicsManagerCommonBase::BeginFrame(frame);
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_NewFrame();
#ifdef OS_WINDOWS
ImGui_ImplWin32_NewFrame();
#endif
}
void OpenGLGraphicsManager::EndFrame(const Frame& frame) {
ImGui_ImplOpenGL3_RenderDrawData(ImGui::GetDrawData());
OpenGLGraphicsManagerCommonBase::EndFrame(frame);
}同样,加粗的部分是插入的ImGui图形API绑定的代码片段。寥寥几行,非常干净。不过原本按照我们的模块划分,RHI里面是不应该有平台相关的代码的。我这里暂时将平台相关代码放在这里,用宏定义标出,今后需要将这一部分进一步整理到Platform下面去。
这样平台及RHI相关的部分就植入完毕了。接下来就是使用了:
Framework/Common/GraphicsManager.cpp
void GraphicsManager::Draw() {
auto& frame = m_Frames[m_nFrameIndex];
for (auto& pDrawPass : m_DrawPasses) {
pDrawPass->BeginPass();
pDrawPass->Draw(frame);
pDrawPass->EndPass();
}
if (ImGui::GetCurrentContext())
{
ImGui::NewFrame();
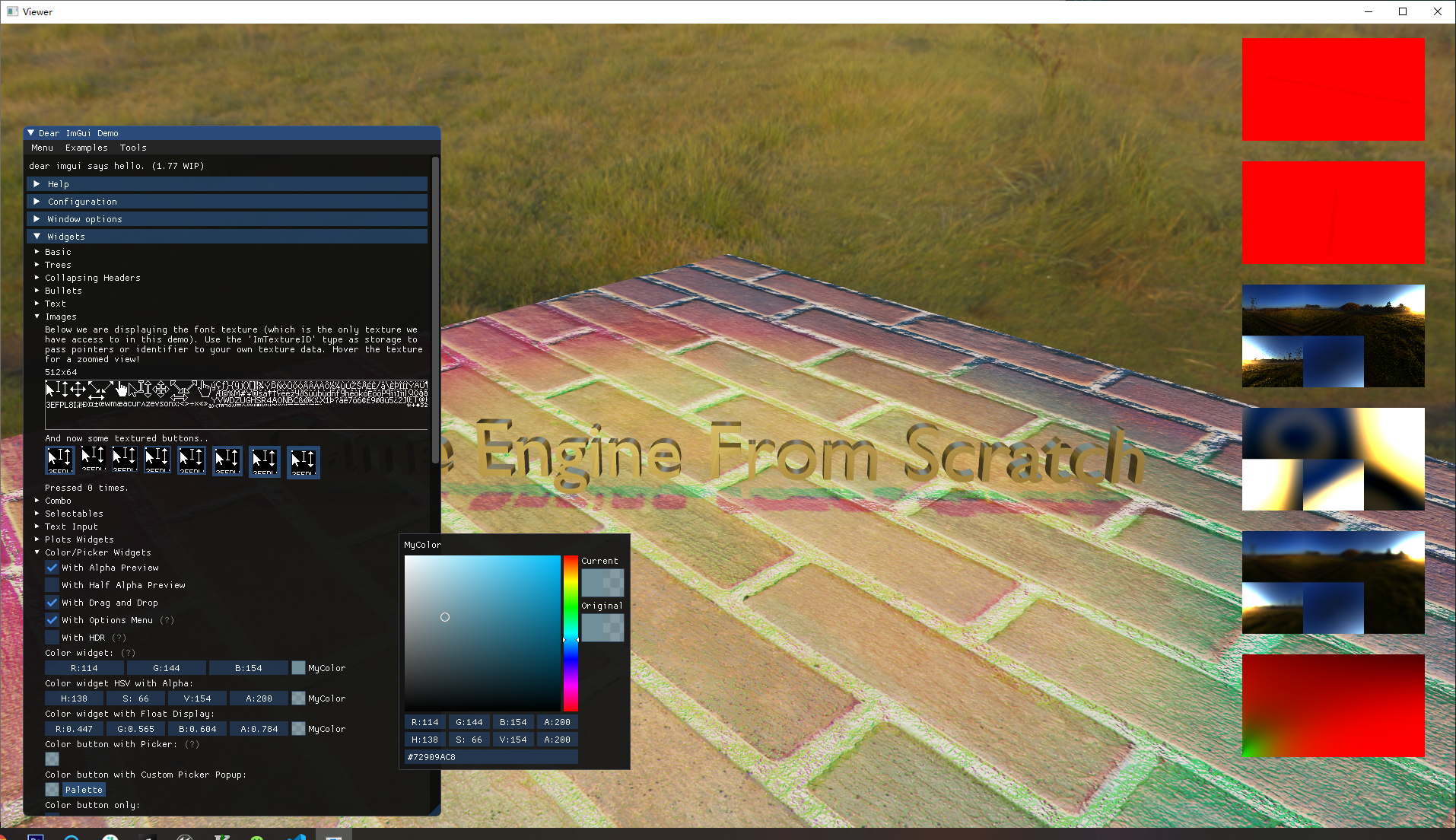
ImGui::ShowDemoWindow();
ImGui::Render();
}
}依然,非常地简单。在场景绘制完成之后,追加GUI绘制的部分就可以了。当然,这部分目前也是临时这么写,根据我们引擎的结构,应该将这部分整理到DrawPass或者DrawSubPass当中去。
接下来我们对应MacOS(OS X)+Metal。基本思路是一样的。首先是平台层面:
Platform/Darwin/CocoaApplication.mm
#include "imgui/examples/imgui_impl_osx.h"
void CocoaApplication::CreateMainWindow() {
[NSApplication sharedApplication];
...
[m_pWindow setTitle:appName];
[m_pWindow makeKeyAndOrderFront:nil];
id winDelegate = [WindowDelegate new];
[m_pWindow setDelegate:winDelegate];
[winDelegate release];
// Initialize ImGui
IMGUI_CHECKVERSION();
ImGui::CreateContext();
[[maybe_unused]] ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
ImGui_ImplOSX_Init();
ImGui::StyleColorsDark();
}
void CocoaApplication::Finalize() {
ImGui_ImplOSX_Shutdown();
[m_pWindow release];
BaseApplication::Finalize();
}
void CocoaApplication::Tick() {
while (NSEvent* event = [NSApp nextEventMatchingMask:NSEventMaskAny
untilDate:nil
inMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode
dequeue:YES]) {
ImGui_ImplOSX_HandleEvent(event, [m_pWindow contentView]);
switch ([(NSEvent*)event type]) {
case NSEventTypeKeyUp:
NSLog(@"[CocoaApp] Key Up Event Received!");
if ([event modifierFlags] & NSEventModifierFlagNumericPad) {
// arrow keys
NSString* theArrow = [event charactersIgnoringModifiers];
unichar keyChar = 0;
然后是RHI层面:
RHI/Metal/Metal2Renderer.mm
#include "imgui/examples/imgui_impl_metal.h"
#include "imgui/examples/imgui_impl_osx.h
- (void)initialize {
[self loadMetal];
ImGui_ImplMetal_Init(_device);
}
- (void)finalize {
ImGui_ImplMetal_Shutdown();
}
- (void)beginFrame:(const My::Frame&)frame {
// Wait to ensure only GEFSMaxBuffersInFlight are getting processed by any stage in the Metal
// pipeline (App, Metal, Drivers, GPU, etc)
dispatch_semaphore_wait(_inFlightSemaphore[frame.frameIndex], DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
// now fill the per frame buffers
[self setPerFrameConstants:frame.frameContext frameIndex:frame.frameIndex];
[self setLightInfo:frame.lightInfo frameIndex:frame.frameIndex];
ImGui_ImplMetal_NewFrame(_mtkView.currentRenderPassDescriptor);
ImGui_ImplOSX_NewFrame(_mtkView);
}
- (void)endFrame:(const Frame&)frame {
// Create a new command buffer for each render pass to the current drawable
_commandBuffer = [_commandQueue commandBuffer];
_commandBuffer.label = @"GUI Command Buffer";
[_commandBuffer enqueue];
if (_renderPassDescriptor) {
_renderPassDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = MTLLoadActionLoad;
_renderPassDescriptor.depthAttachment.loadAction = MTLLoadActionLoad;
_renderEncoder = [_commandBuffer renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor:_renderPassDescriptor];
_renderEncoder.label = @"GuiRenderEncoder";
ImGui_ImplMetal_RenderDrawData(ImGui::GetDrawData(), _commandBuffer, _renderEncoder);
[_renderEncoder endEncoding];
}
[_commandBuffer presentDrawable:_mtkView.currentDrawable];
// Add completion hander which signals _inFlightSemaphore when Metal and the GPU has fully
// finished processing the commands we're encoding this frame.
__block dispatch_semaphore_t block_sema = _inFlightSemaphore[frame.frameIndex];
[_commandBuffer addCompletedHandler:^(id<MTLCommandBuffer> buffer) {
dispatch_semaphore_signal(block_sema);
}];
[_commandBuffer commit];
}有几个需要注意的点:
- ImGui_ImplMetal_NewFrame(_mtkView.currentRenderPassDescriptor)当中使用了 _weak 关键字,但是我们的代码没有使用ARC,所以编译会报错。解决的方法是在CMake当中追加如下属性打开Clang的一个编译选项:
set_property (TARGET MetalRHI APPEND_STRING PROPERTY COMPILE_FLAGS "-fobjc-weak") - Metal的renderEncoder会在开始的时候对attachment执行制定的loadAction。缺省为Clear。所以需要将其手动指定为MTLoadActionLoad来避免场景渲染结果被清除。
下面是执行效果。和Windows上是一致的。