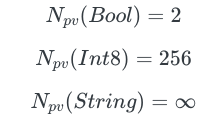Swift 的 Enums 是 “Sum” 类型,这让一切变得更有趣
简评:代数类型并不是专指某种类型,而是对原有类型的一种思考方式。Sum 类型是代数类型的一种,合理的使用 Sum 类型,能让代码的可读性大大提高。
代数类型 - 它们是什么?
代数类型并不是一种新类型,而是一种思考方式。
有许多不同的代数类型,实际上你当前使用的所有类型都是代数的。 在这里我们介绍两
种基本的代数类型:
- Product 类型
- Sum 类型
所以让我们从熟悉的东西开始吧。
Product 类型
Swift 的 struct 和 Java 的 class 都算是 Product 类型。
它们被称为 Product 类型是因为它们具有的可能值的数量是其组成部分的可能值的数量的乘积(这句话不好理解,可以直接看示例)。
struct ProductExample {
let a: Bool
let b: Bool
}
所以 Bool 类型可以有 2 种可能。 ProductExample 中包含 2 个 Bool 类型的值 a, b。所以 ProductExample 有 4 (2 x 2) 种可能。
这种类型的所有可能的情况很明显:
let first = ProductExample(a: true, b: true)
let second = ProductExample(a: true, b: false)
let third = ProductExample(a: false, b: true)
let fourth = ProductExample(a: false, b: false)
我们来看另一个例子:
struct ProductExampleTwo {
let a: Bool
let b: Int8
}
现在我们看看 ProductExampleTwo 具有几种可能,它包含 Bool 和 Int8 的类型。 Int8 有 256
种可能, Bool 有 2 种可能 。 所以我们的 ProductExampleTwo 有 512 (2 x 256) 种可能。
我们可以定义一个函数 Npv 用于返回某个类型可能值的数量。
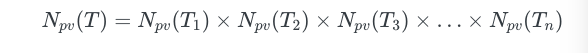
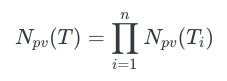
Sum 类型
Swift 中的 Enum 就是典型的 Sum 类型,举个例子:
enum SumExample {
case a(Bool)
case b(Bool)
}我们可以列举出 SumExample 所有的情况:
let first = SumExample.a(true)
let second = SumExample.b(true)
let third = SumExample.a(false)
let fourth = SumExample.b(false)可以看出,Enum 可能值的数量为 Enum 所有组成部分可能值数量之和,所以 Npv(SumExample) 结果是 Npv(Bool) + Npv(Bool) = 2 + 2 = 4。
再举个例子:
enum SumExampleTwo {
case a(Bool)
case b(Int8)
}
Npv(SumExampleTwo) = Npv(Bool) + Npv(Int8) = 2 + 256 = 258。
我们如何利用这种特点写出更好的代码?
1. 使用 Enum 作为返回值:
如果我们定义了一个方法发送一个请求并返回一个 String 类型的结果,我们来看看以前常见的代码。
typealias Handler = (String?, Error?) -> Void
func getUser(from: URL, completionHandler: Handler) {
// function implementation
}
getUser(from: someUrl) { result, error in
if let result = result {
// Handle result
}
if let error = error {
// Handle error
}
}
为什么这是一个坏的选择? 因为我们的返回值只有两种可能的情况:
- success - 从服务器获取结果
- fail - 函数处理过程中出现的错误
看到这段代码,在不熟悉业务的情况下我们根据返回值会做如下 4 种判断:
result = nil, error = not nil // Case 1
result = not nil, error = nil // Case 2
result = not nil, error = not nil // Case 3
result = nil, error = nil // Case 4但实际上成功失败仅仅只需要两种可能:
成功:result != nil, error == nil
失败:result == nil, error != nil
这个问题的原因是我们使用了 Product 类型而不是 Sum 类型。
把返回值换成 enum 的代码现在是这样的。
enum Result {
case success(String)
case error(Error)
}
typealias Handler = (Result) -> Void
func getUser(from: URL, completionHandler: (Handler)) {
// implementation
}
getUser(from: someUrl) { response in
switch response {
case .success(let result):
print(result)
case .error(let error):
print(error.localizedDescription)
}
}我们创建了一个称为 Result 的 Sum 类型,我们使用它来区分两种可能性。 我们的用例符合我们的实际情况,这样非常的棒。
2. Optional enum
Swift 最常用的一种类型 - Optional,内部就是使用 Sum 类型 Enum 来实现的:
enum Optional<T> {
case some(T)
case none
}所以 let a: String? = "Hello" 这段代码,只是 let a = Optional.some("Hello") 这段代码的简写。
好消息是,Swift 有一些简洁的语法糖来帮助我们区分 Sum 类型- if let 和 guard let 结构。
let a: String? = "Hello"
if let a = a {
print(a)
} else {
print("error")
}
相当于:
let a = Optional.some("Hello")
switch a {
case .some(let res):
print(res)
case .none:
print("Error")
}
3. 使用 Sum 类型来表示路由
在你的应用程序中,有些东西的可能性是有限的,并且非常容易用 Sum 类型表示出来。例如使用 enum 来表示不同的网络请求的:
enum Router {
case user(id: Int)
case weather(day: Day)
}
extension Router {
var url: String {
switch self {
case .user(let id):
return "\(App.BaseUrl)/user/\(id)"
case .weather(let day):
return "\(App.BaseUrl)/weather/\(day.rawValue)"
}
}
}你的 Router 可以使用这种方式暴露所有东西如参数、请求头、请求类型等。
现在,如果你替换应用主题风格,可以试试这种方式:
struct AppThemeModel {
let baseColor: UIColor
let backgroundColor: UIColor
let accentColor: UIColor
let baseFont: UIFont
}
enum AppTheme {
case dark
case light
var model: AppThemeModel {
switch self {
case .dark:
return AppThemeModel(
baseColor: .red
backgroundColor: .darkRed
accentColor: .yellow
baseFont: .systemFontOfSize(12)
)
case .light:
AppThemeModel(
baseColor: .white
backgroundColor: .gray
accentColor: .blue
baseFont: .systemFontOfSize(13)
)
}
}
}
// During app init
var currentAppTheme = AppTheme.dark4. 实现数据结构
在 swift 中使用 sum 类型来实现树和链表非常容易。
indirect enum Tree<T> {
case node(T, l: Tree, r: Tree)
case leaf(T)
var l: Tree? {
switch self {
case .node(_, l: let l, _):
return l
case .leaf(_):
return nil
}
}
var r: // equivalent implementation to l
var value: T {
switch self {
case .node(let val, _, _):
return val
case .leaf(let val):
return val
}
}
}
let tree = Tree.node(12, l: Tree.leaf(11),
r: Tree.node(34, l: Tree.leaf(34),
r: Tree.leaf(55)))原文:Swift Enums Are “sum” Types. That Makes Them Very Interesting
推荐阅读:FaceApp | 笑着活下去
欢迎关注:知乎专栏「极光日报」,每天为 Makers 导读三篇优质英文文章。